A price floor set below the equilibrium will result in a surplus.
A price floor set below the equilibrium price will result in a surplus true false.
A price ceiling imposed above the market equilibrium price will result in a shortage of the product.
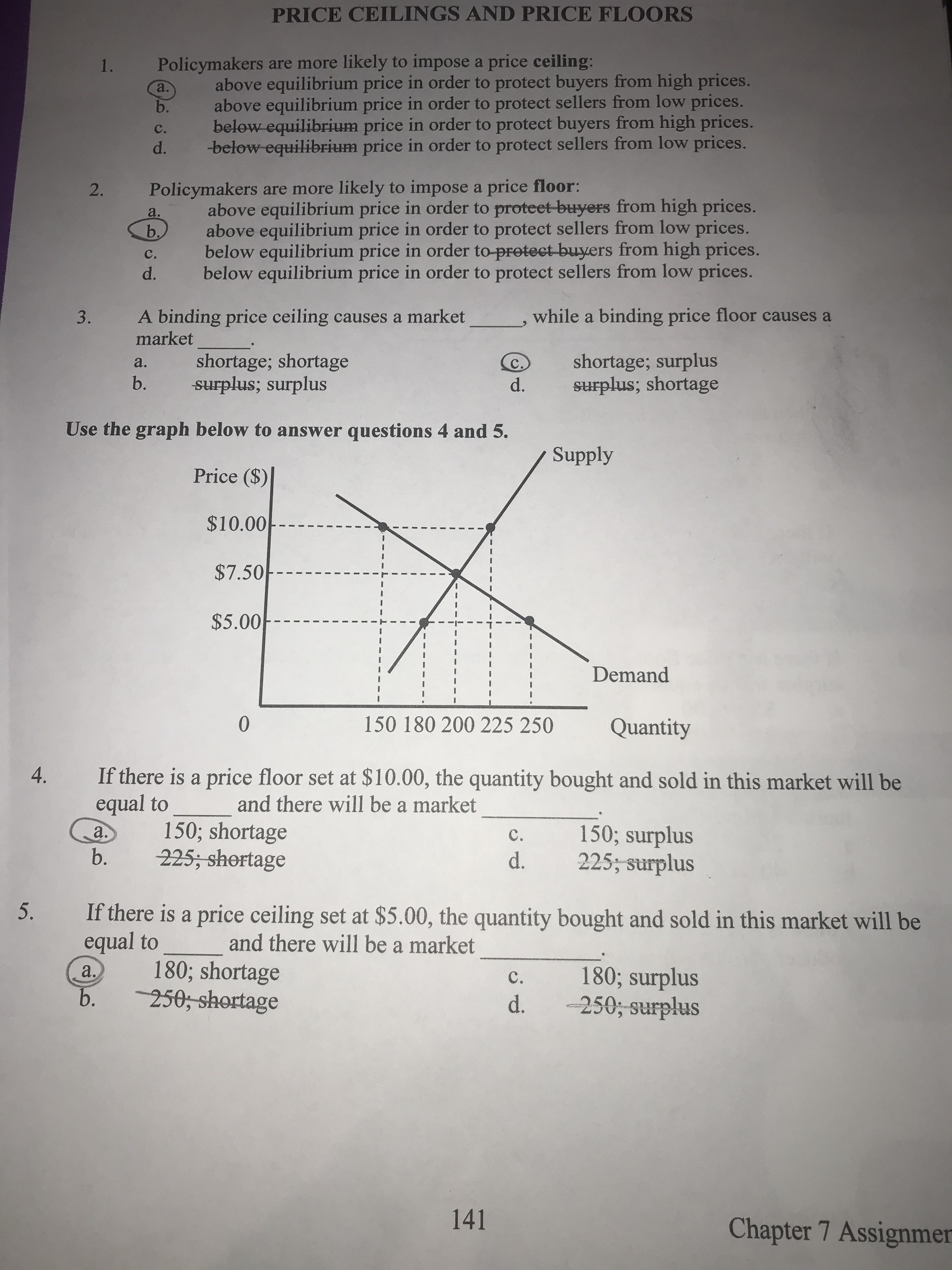
Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level.
Price and quantity controls.
The effect of government interventions on surplus.
A price floor must be higher than the equilibrium price in order to be effective.
Price ceilings and price floors.
Price floors prevent a price from falling below a certain level.
A price ceiling set above the equilibrium price is not binding.
Taxation and dead weight loss.
Example breaking down tax incidence.
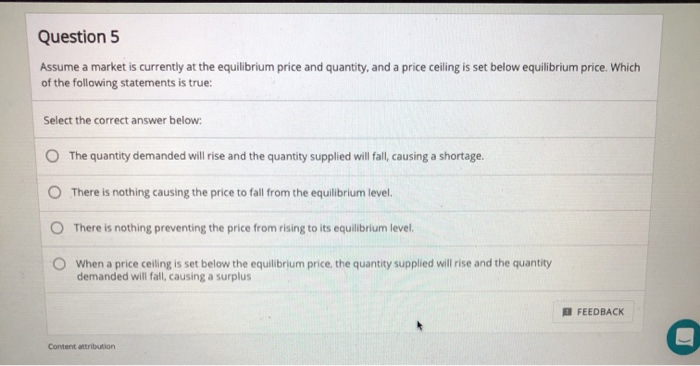
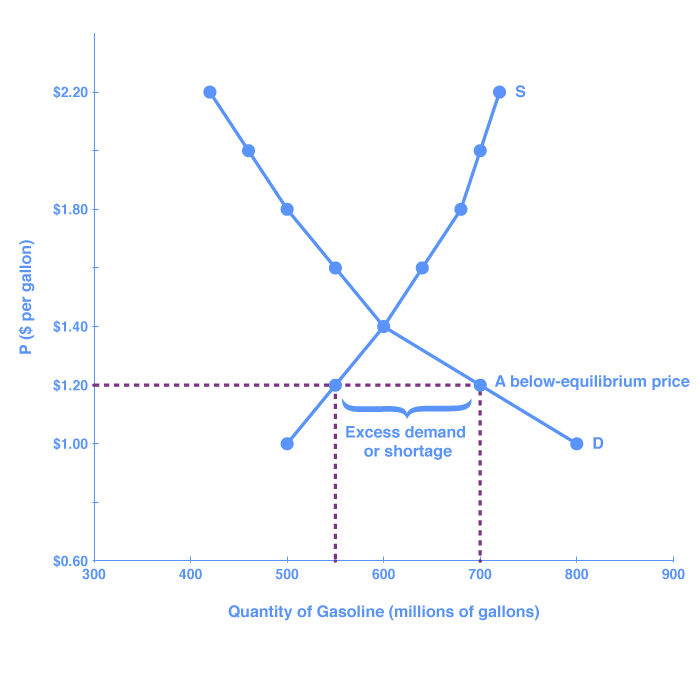
When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price quantity demanded will exceed quantity supplied and excess demand or shortages will result.
A price floor is a government or group imposed price control or limit on how low a price can be charged for a product good commodity or service.
If the equilibrium price of gasoline is 3 00 dollars per gallon and the government places a price ceiling on the gasoline of 4 00 dollars per gallon the result will be a shortage of gasoline.
False shortage as the real wage increases the opportunity cost of not working outside the home increases.
This is the currently selected item.
The equilibrium price commonly called the market price is the price where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external.