If it s not above equilibrium then the market won t sell below equilibrium and the price floor will be irrelevant.
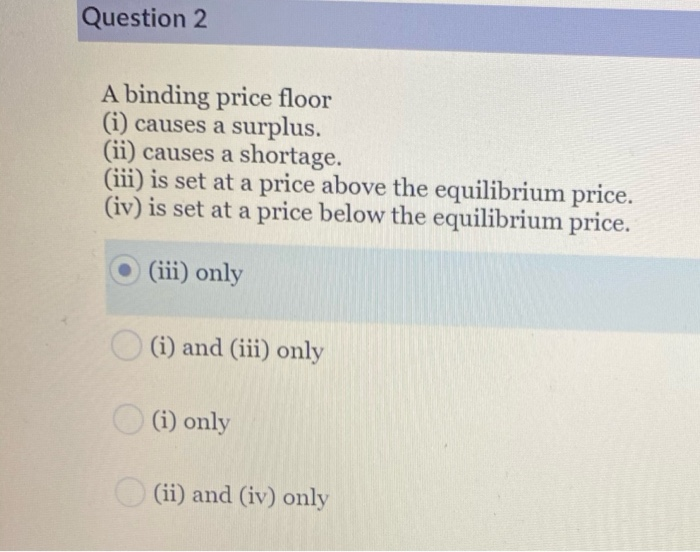
A price floor set above the equilibrium price is binding.
This has the effect of binding that good s market.
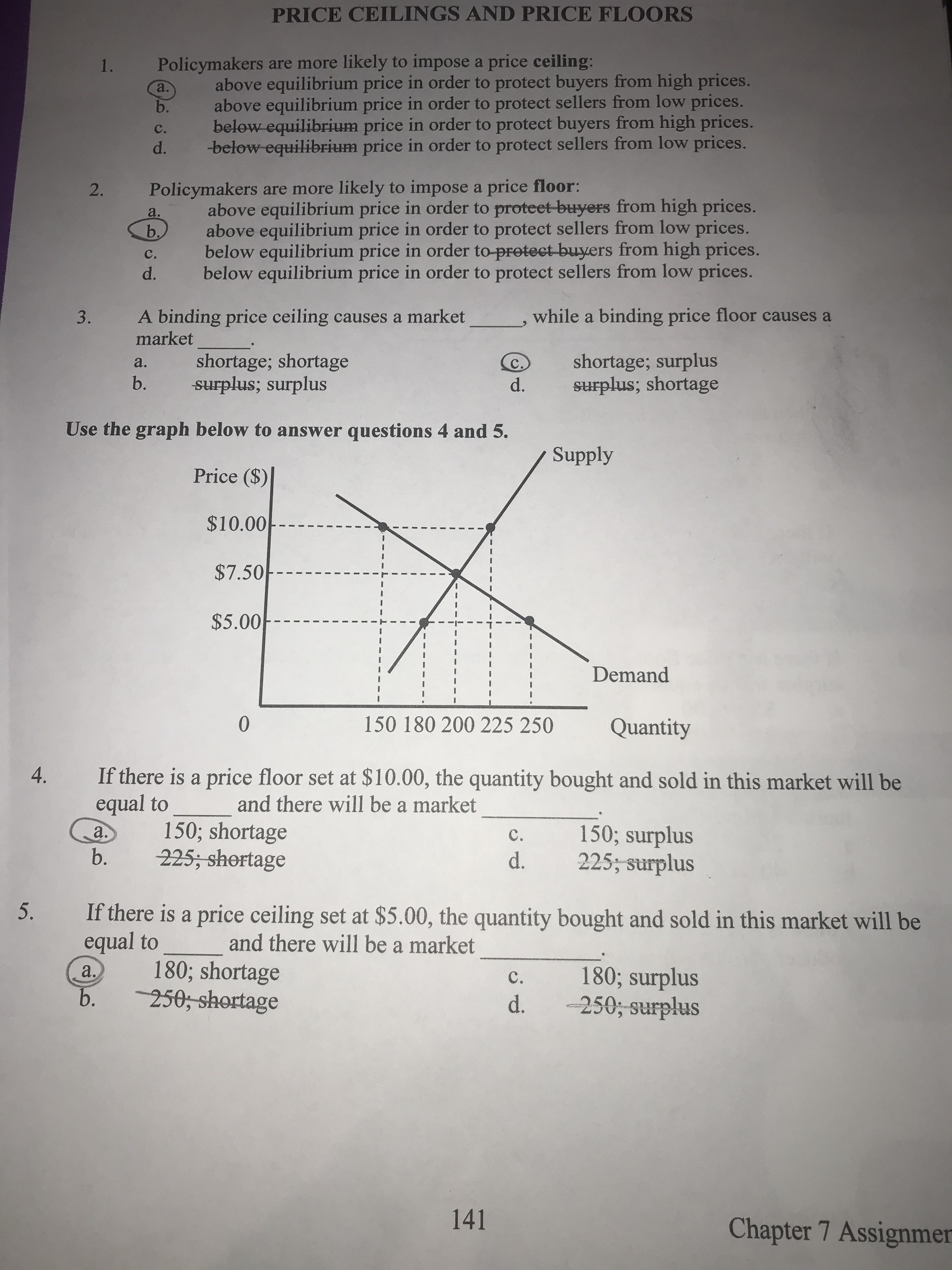
To be binding a price floor must be set at a price.
The equilibrium price is above the price floor.
More than one of the above is correct.
The equilibrium price commonly called the market price is the price where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external.
When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price as in this example it is considered a binding price floor.
It has no legal enforcement mechanism.
A price floor is a government or group imposed price control or limit on how low a price can be charged for a product good commodity or service.
An example of price floor.
The government is inflating the price of the good for which they ve set a binding price floor which will cause at least some consumers to avoid paying that price.
Trading at a lower price is illegal.
A price floor must be set above equilibrium a price ceiling must be set below equilibrium.
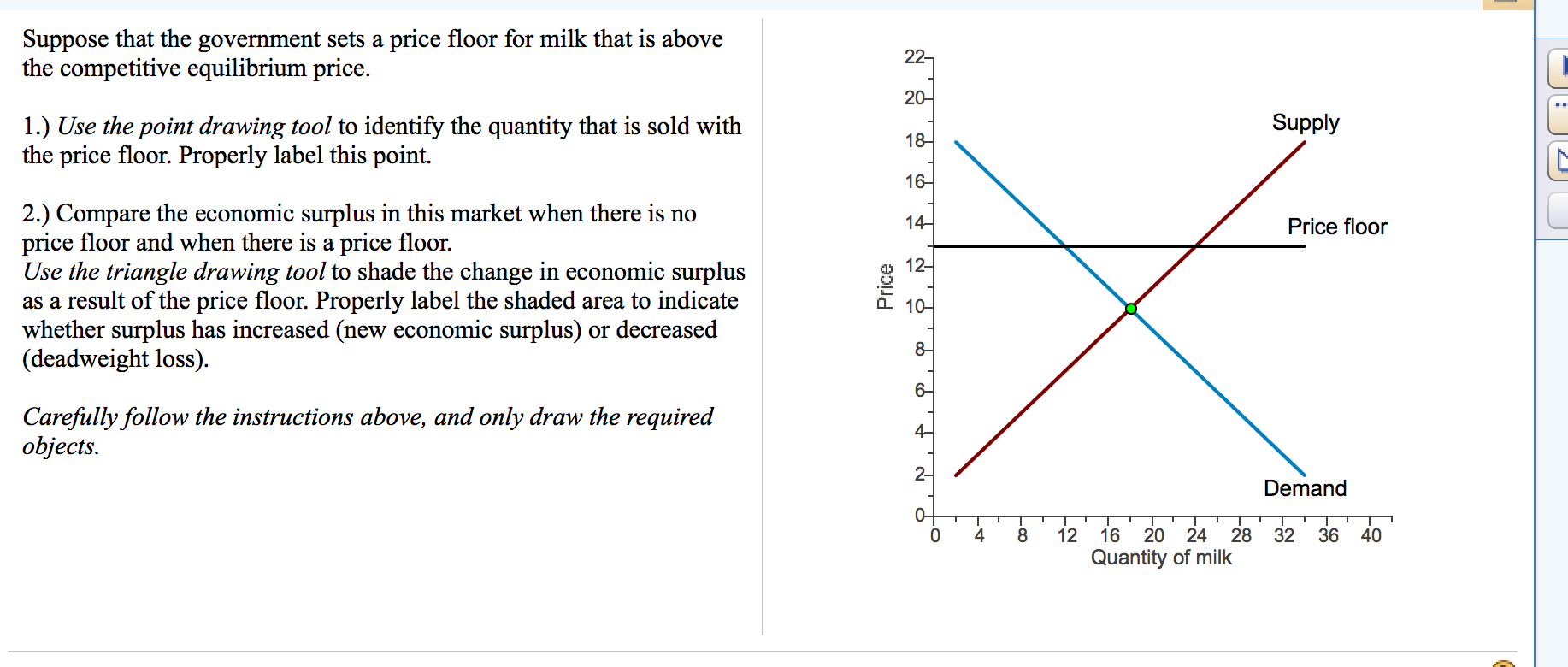
This graph shows a price floor at 3 00.
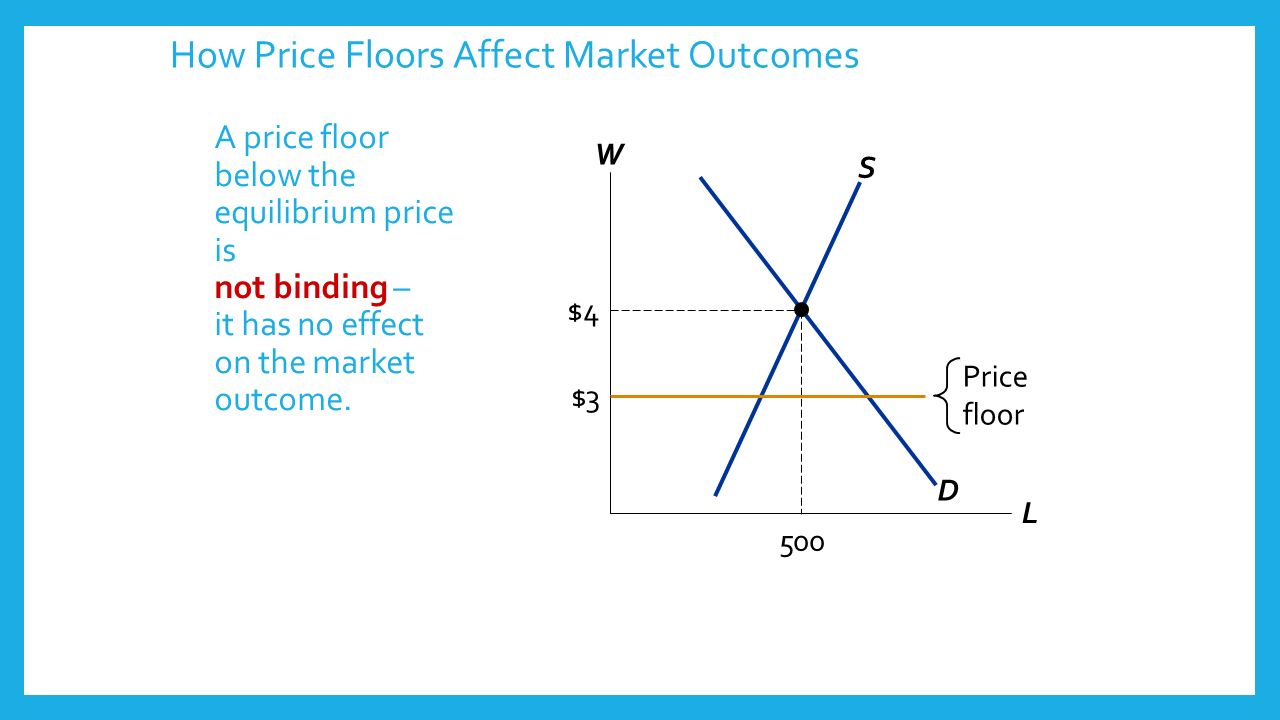
A price ceiling set above the equilibrium price is not binding.
Drawing a price floor is simple.
T f a price floor is a legal minimum on the price at which a good or service can be sold.
If a price floor is not binding then a.
An example of price ceiling.
Higher than the equilibrium price.
For a price floor to be effective it must be set above the equilibrium price.
If a country has the comparative advantage in producing wooden furniture then with free trade.
The result is a quantity supplied in excess of the quantity demanded qd.
True t f to be binding a price floor must be set above the equilibrium price.
When quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded a surplus exists.
Price floors prevent a price from falling below a certain level.
Simply draw a straight horizontal line at the price floor level.
What makes a price floor price ceiling binding effective.
Price ceilings prevent a price from rising above a certain level.
The equilibrium price is below the price floor.
A price floor must be higher than the equilibrium price in order to be effective.